Let’s be honest—redirects sound boring until one wrong move tanks your site traffic. Ever swapped a URL, did a quick redirect, and suddenly things got weird in Google…or your forms stopped working?
I’ve been there, and if you’re reading this, you’re probably about to make a change—maybe it’s a site migration, a limited-time promo, or just fixing a broken page. Whatever the reason, the “which redirect should I use?” rabbit hole gets messy, fast. So let’s keep it real and practical.
This guide is for anyone who’s had to Google “ Redirect: 301 vs 302 vs 307” at midnight because they didn’t want to break SEO or mess up user experience again. You’ll get exactly what you need—clear differences, real-world scenarios, honest lessons learned—without the tech jargon.
What Is a Redirect? Quick Overview & Types of HTTP Status Codes
A redirect simply guides visitors (and search engines) from one URL to another—think of it like a sign saying, “We’ve moved!”
The three most common redirects:
- 301: Permanent move—use when you change URLs or merge pages for good.
- 302: Temporary move—great for tests, short promos, or quick maintenance.
- 307: Also temporary, but keeps the original request method (handy for forms and technical stuff).
Redirects keep your visitors on track and help Google understand changes. For the real SEO impact and how to choose the right type, check out the next sections!
If you want to fully understand how to audit your SEO before making redirects, check out this SEO technical audit guide to avoid costly mistakes. One more thing, redirects are also a key part of effective SEO techniques you should know.
Quick Comparison Table Redirect: 301 vs 302 vs 307
| Redirect Type | Status | When to Use | SEO Impact / Link Juice | HTTP Method Preserved? |
| 301 | Permanent | Moving content, merging pages | Passes link equity (“juice”) | No (can change POST to GET) |
| 302 | Temporary | Sales, maintenance, A/B tests | Usually passes link equity* | No (may switch POST to GET) |
| 307 | Temporary (but strict) | When method must stay the same (forms, APIs) | Treated like 302 (temporary), link juice usually preserved* | Yes (POST stays POST) |
Deep Dive: 301 Redirect (How It Works & SEO Impact)
Let’s talk straight: when you hit the big red “301” button, you’re telling both visitors and Google, “Hey, that old page? It’s out. Here’s the new spot, for good.”
I remember the first time I did this. I was merging two messy old blog posts into one better guide. Heart in my throat—I wanted the SEO to follow, not flatline. Here’s what actually happens:
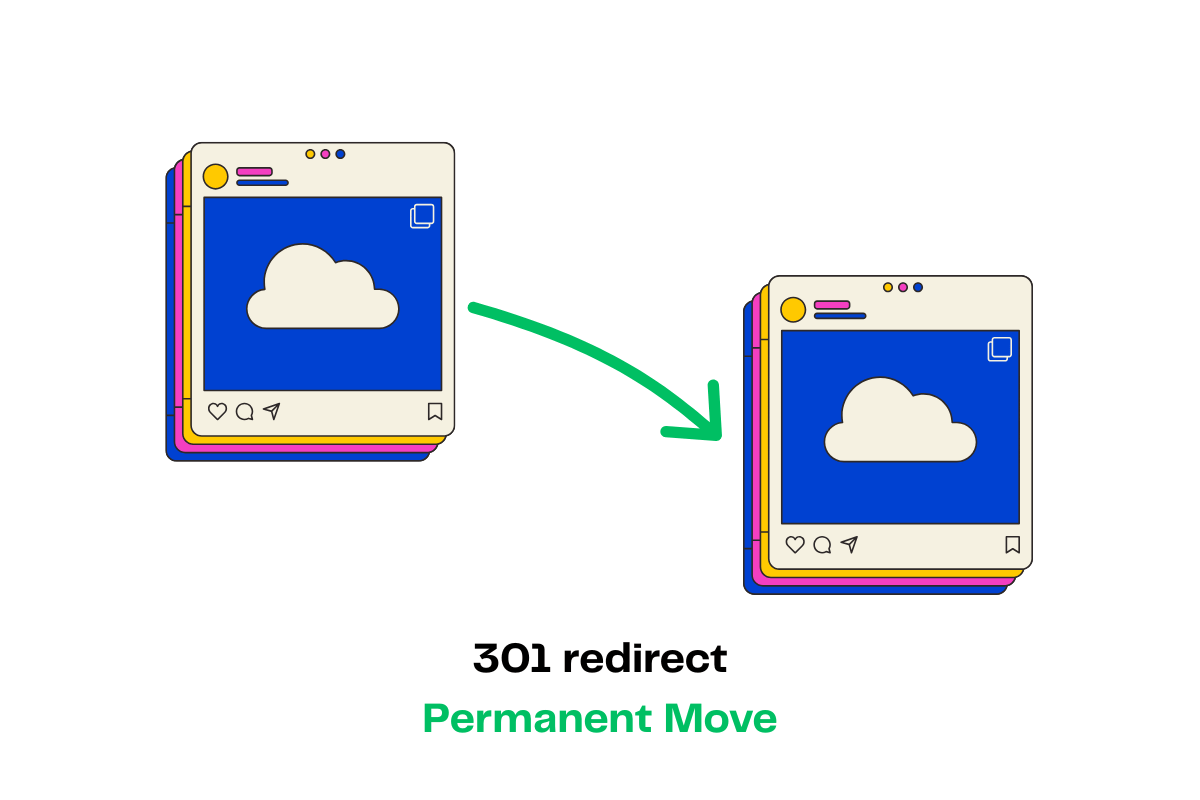
301 = Permanent Move: Think of it like forwarding mail when you move house. Google gets the message—your content, ranking, and “link juice” flow to the new page, not down the drain.
Why does it matter for SEO? Do it right, and you keep your spot (and sometimes, climb a bit higher). Mess it up—like forgetting internal links, or breaking the redirect chain—and you can lose traffic fast. I’ve seen sites dip 20% in a week, sometimes more.
Pro lesson: Batch moves are riskier. Once, I redirected an entire category tree at once, thinking, “Google’s smart, it’ll sort it out!” Traffic tanked for two months. Next time, I staged things, checked Search Console daily, and the recovery was way smoother.
Real insight:
A 301 is powerful, but it’s not magic. Prep with a checklist, track results, and never assume rankings will just ‘stick’ overnight. The work doesn’t end after you hit save.
If you’re ever unsure, test on a less critical page first. That little extra step can save a lot of headaches—and maybe even your site’s momentum
Deep Dive: 302 Redirect (When to Use & Key Notes)
A 302 redirect simply means: “This move isn’t forever—check back soon.” It’s what you use when you want people (and Google) to treat the new page as a pit stop, not a permanent home.
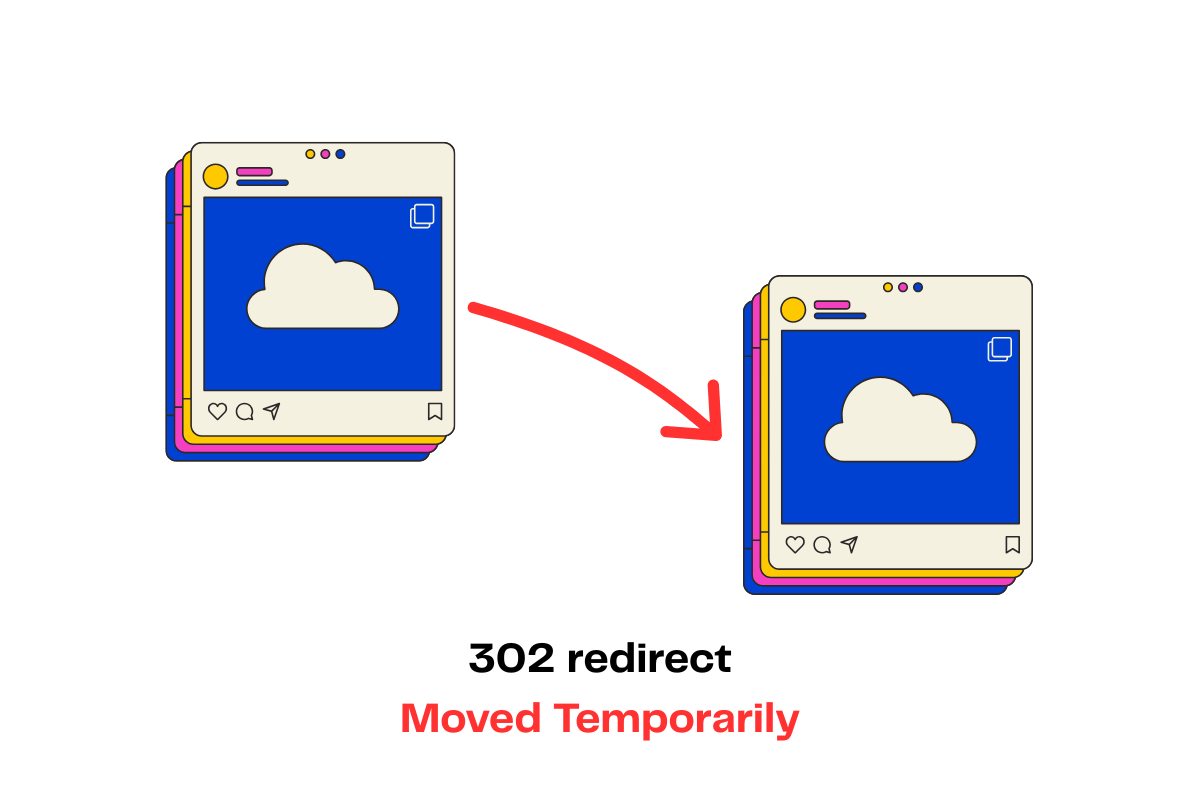
Best times to use a 302:
- You’re running a flash sale and want product A to briefly lead somewhere special.
- Doing site maintenance, but don’t want Google to forget your original content.
- Testing out a new landing page with A/B experiments.
From experience? I once had a big promo on a client’s homepage, set up a 302 redirect to the campaign page, and after the event ended, we switched the redirect off—no harm done, rankings and traffic picked right up where they left off.
But here’s the pitfall: I’ve also seen someone forget to change a 302 to a 301 after completing a permanent domain move. Result? Google kept showing the old URL in search, and it took weeks for rankings to recover when we fixed it.
Deep Dive: 307 Redirect (Special-Case Redirects)
A 307 redirect is your tech-savvy safety net—it’s like saying, “We’re moving, but please keep everything just as you left it.” The magic? It preserves the HTTP method.
That sounds technical, but here’s why it matters:
Ever filled out a long form (maybe a checkout or sign-up), hit submit, and wonder if a detour would eat your data? With 301 or 302, sometimes those POST requests flip to simple GETs behind the scenes—and suddenly, info gets lost. A 307 guarantees that what goes in, comes out unchanged.
When do you actually use a 307?
- When forms, payments, or logins are at stake—basically, moments when you absolutely cannot risk breaking data flow.
- For temporary API reroutes (think: moving traffic without rewriting every endpoint).
- When tight security rules mean even a tiny method change could break things.
A quick lesson: I once watched a developer nearly tear their hair out because a “simple redirect” broke every checkout on a busy sale day. Swapping their 302 for a 307 fixed it instantly—orders flowed, the sighs of relief were real.
Choosing the correct redirect isn’t just a technical detail—it’s the safety net for your site’s traffic, rankings, and user trust. Here’s a practical checklist to help you nail the decision every time. (Yes, this is the step where you pause and double-check before you hit save.)
Redirects & SEO: Link Juice, Indexing, Analytics
Do Redirects Pass Link Juice for Real?
- 301 passes almost all SEO value—done deal.
- 302/307? If used for a while, Google will usually transfer authority too (but don’t risk them for permanent moves).
Simple: if you want your rankings safe, pick 301 for anything permanent.
Temporary? 302 or 307 does the trick without drama.
Indexing: How Fast Does Google Catch Up?
Don’t expect changes overnight. Sometimes your new URLs start showing in Google within days, but a big site or lots of redirects can mean weeks.
To speed things up, I always submit updated URLs in Search Console—and keep an eye out for any forgotten old links or errors.
Analytics Can Get Weird—Here’s How to Stay Sane
Redirects can make reporting messy if you’re not ready for them.
Sometimes GA4 or Universal Analytics “split” your new and old URLs, so numbers look off. I always place an annotation for redirect launches in my analytics—future me is grateful!
Had an embarrassing moment once when conversions seemed to drop to zero—turns out, the goal URLs just changed with the redirect. Quick fix, but scary for a night.
How to Set Up Redirects in WordPress (301/302/307)
Most site owners use plugins for redirects. It’s safer, easier, and works for 301, 302, or even 307—no tech headaches!
The Redirection plugin is the go-to tool. Here’s how you do it:
- Install the Redirection Plugin
-
-
- Go to your WordPress dashboard.
- Click Plugins > Add New.
- Search for “Redirection”. Hit Install then Activate.
-

- Set Up Your Redirect
-
-
- In your dashboard, find Tools > Redirection.
- Follow the welcome/setup screens (takes less than a minute the first time).
- Scroll to Add new redirection.
- Enter your Source URL (the old link) and the Target URL (where you want people to go).
-
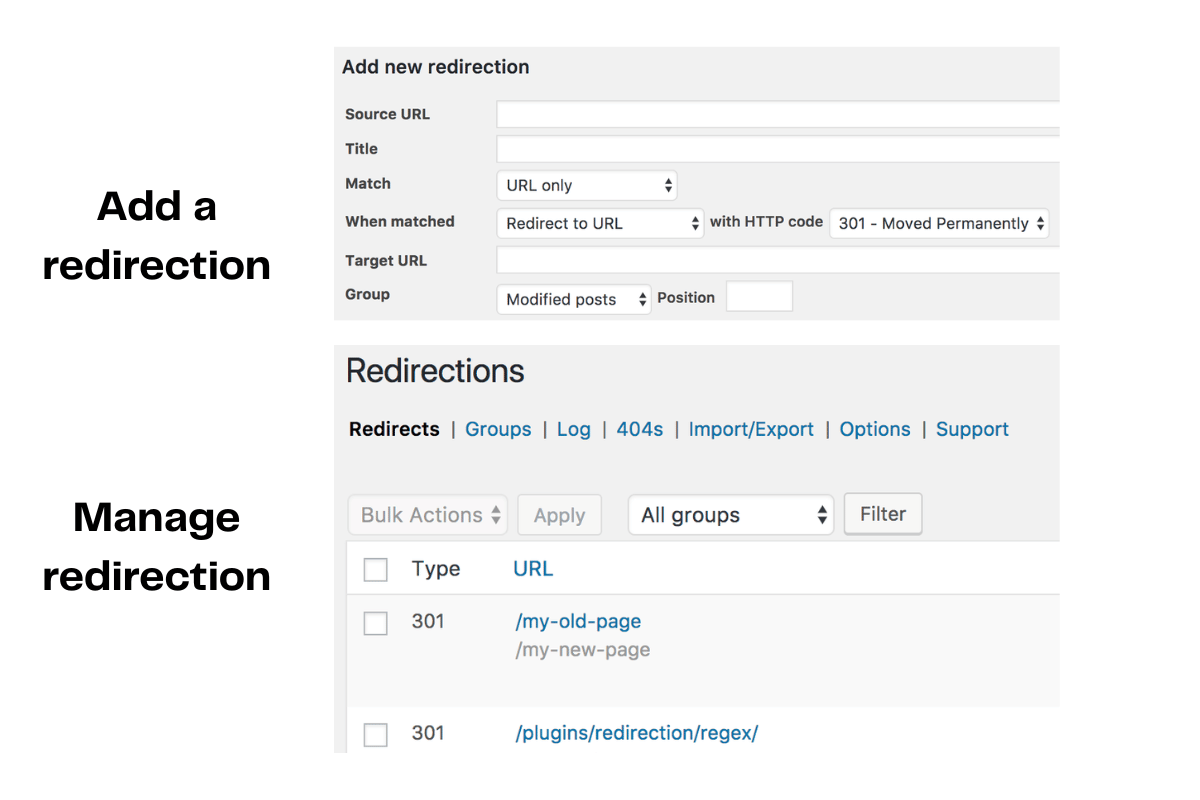
- Choose Redirect Type
-
-
- Click the gear icon if you want to change from the default 301.
- Select 301 for permanent, 302 or 307 for temporary needs.
-
- Save and Test
-
- Click Add Redirect.
- Test your old link in a browser—if it jumps to the new URL, done!
Checklist: How to Choose the Right Redirect
1. Is the change permanent or temporary?
- Permanent: The old page is never coming back, and you want Google and users to treat the new location as the “real” one.
- Use: 301 Redirect
- Temporary: You plan to bring the original page back (think sales, maintenance, tests).
- Use: 302 or 307 Redirect
2. Are there any forms or special methods involved? (e.g., payment, sign-up, complex forms)
- Yes: You need to keep the exact HTTP method (POST stays POST).
- Use: 307 Redirect
- No: Regular “click-and-go” page, no sensitive data.
- Use: 301 or 302 as above
3. Do you want to pass SEO value and link equity to the new page?
- Yes, and it’s permanent:
- 301 gives the strongest signal to pass link equity (“juice”), but Google now often passes equity with 302/307 if you don’t later switch back.
- Yes, but temporary:
- 302 or 307. Google will usually return equity to the original when you switch back.
4. Is this for a site migration or content merge?
- Moving or consolidating pages or domains for good?
- Always lean 301.
- Testing new layouts or offers?
- Use 302 or 307, depending on method needs.
5. Are you handling a critical business process (checkout, API, member actions)?
If there’s any risk to user data or actions, default to 307 (to avoid method-switch errors)
Absolutely—here’s a snappier rewrite for the “Do Redirects Pass Link Juice for Real?” part, while keeping the rest of the section at regular length and detail.
Common Redirect Mistakes (and How to Fix Them)
Let’s be honest: I’ve made every redirect mistake in the book—and felt the pain in traffic, rankings, and confused analytics. Here’s how you avoid the same headaches:
1. Redirect Chains & Loops
Ever set up a redirect and realize it goes from A → B → C… or worse, loops right back? Google will try crawling, get tired, and maybe just give up. Result: traffic nosedive, pages lost from the index.
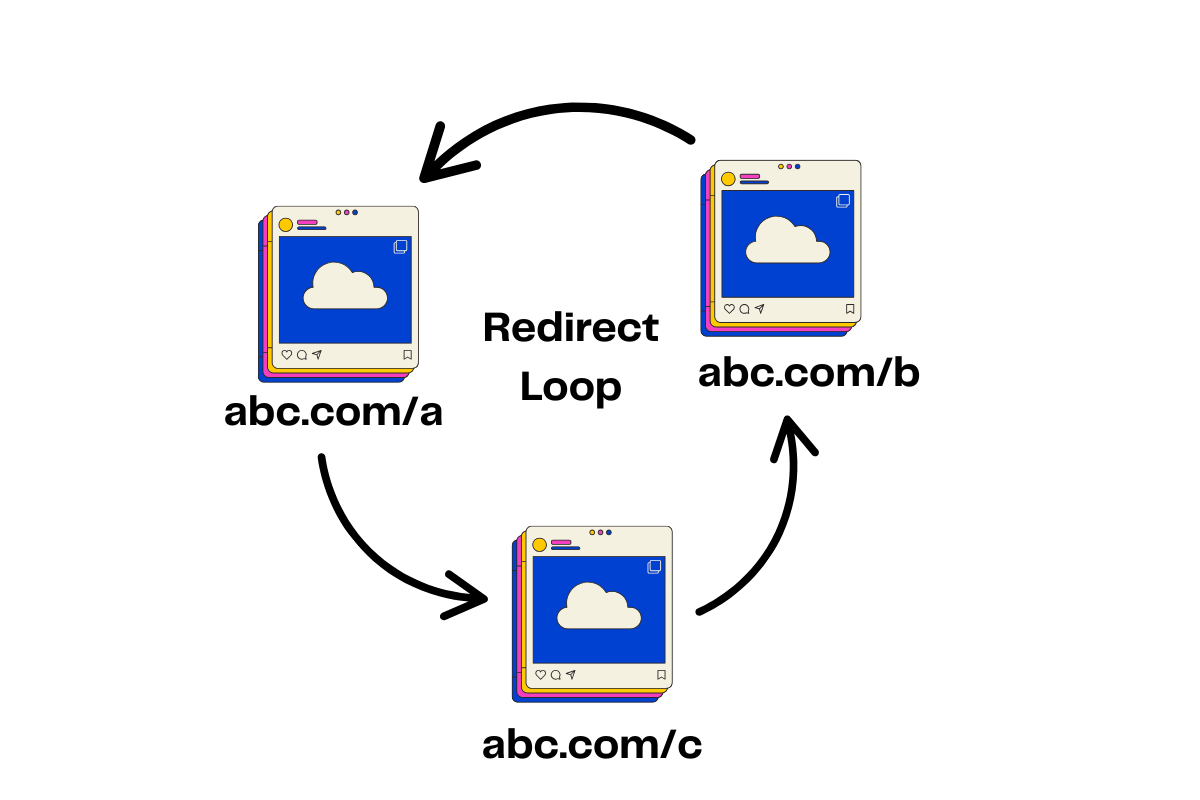
How to fix it:
- Always map redirects directly (A → B), no unnecessary detours.
- Use tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs to scan for chains and loops.
- Check in Search Console if Google is getting stuck, then clean up broken paths right away.
2. Using the Wrong Redirect Type (301 for Temporary, 302 for Permanent)
Mix these up, and both users and Google get confused. I’ve seen sites stuck with old URLs still showing in Google weeks later—or PageRank just vanishing.
How to fix it:
- Use the checklist above every time: 301 for permanent moves, 302/307 for temporary.
- If you catch a mistake, update your redirects and nudge Google (resubmit in Search Console).
- A quick audit saves weeks of recovery.
3. Missing Internal Updates (Links, Sitemap, Canonical Tags)
Redirect set? Great. But if your internal links, sitemap, or canonical tags still point to the old URL, you’re sending mixed signals—and trust me, Google hates being confused.
How to fix it:
- Scan through your entire site for old links after major redirects.
- Update your sitemap and resubmit it in Search Console.
- Double-check canonical tags—they should always point to your preferred (new) URL.
Redirects look simple—until you see your rankings drop. Take a breath, check your redirect type, and fix mistakes fast. It’s not about being perfect the first time, it’s about spotting errors early and bouncing back before your traffic takes a hit.
And if you ever want zero guesswork? The Golden Owl Digital team is always ready to jump in, fix the technical stuff, and keep your SEO safe.

Jaden is an SEO Specialist at Golden Owl Digital. He helps brands rank higher with technical SEO and content that resonates