Get insights on how are software companies valued and learn how to enhance your SaaS business’s multiplier. Focus on retention, reduce churn, and increase profitability.
Let’s start.
How Are Software Companies Valued Differently?
SaaS companies have unique features that make their valuation different from traditional software businesses. The primary distinction lies in their business model, which relies on recurring revenue rather than one-time sales.
Here’s a breakdown of these differences:
1. Recurring Revenue Models
SaaS companies usually operate on subscription or usage-based pricing, generating monthly recurring revenue (MRR) or annual recurring revenue (ARR).
This recurring revenue is highly valued because it provides consistent and predictable income. When subscribers commit to multi-year subscriptions, ARR is the preferred measure. MRR is more relevant for startups or businesses with monthly renewal subscribers.
Traditional software companies, on the other hand, often rely on one-time sales, leading to fluctuating and less predictable revenue.
2. Scalability and Growth Potential
The scalability of SaaS companies is another key factor that sets them apart. SaaS businesses can scale rapidly without significant increases in operating costs, due to the cloud-based nature of their services. This allows them to add new customers with minimal incremental expenses.
Following scalability, companies with high growth rates and scalable operations attract higher valuation multiples. For example, SaaS companies with ARR of $10 million or more often receive valuation multiples between 10x and 15x, reflecting their growth potential and market appeal.
3. Customer Retention and Churn Rates
Customer retention is crucial for SaaS companies and directly impacts their valuation. Lower churn rates (the rate at which customers leave) and higher net revenue retention (NRR) rates indicate a loyal customer base and steady revenue.
For instance:
- A good NRR for enterprise SaaS companies is around 125%;
- A healthy NRR for small to medium-sized business (SMB) SaaS is about 90%.
High retention and low churn mean the company doesn’t need to constantly find new customers, making it more stable and attractive to investors.
4. Market Position and Competitive Landscape
The competitive position of a SaaS company also affects its valuation. Companies that have found a good market fit and established themselves as leaders in their niche tend to get higher valuations. Strong market position and competitive advantages make these companies appeal to be lower-risk investments with higher growth potential.
5. Financial Metrics and Efficiency
SaaS companies are often evaluated based on key financial metrics such as gross margins, customer acquisition costs (CAC), and lifetime value (LTV). These metrics are crucial for investors assessing the financial health and future profitability of a SaaS business.
High gross margins, typically around 80% or more, indicate efficient operations and the ability to reinvest profits into growth. Additionally, favorable CAC to LTV ratios demonstrate the company’s efficiency in acquiring and retaining profitable customers.
To sum up, here is a table of the key differences in valuing SaaS companies compared to traditional software businesses:
| Factor | SaaS Companies | Traditional Software Companies |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue Model | Subscription-based or usage-based, generating MRR/ARR | One-time sales or licensing fees |
| Revenue Predictability | High due to recurring revenue | Low due to reliance on one-time sales |
| Scalability | High, can add customers with minimal incremental costs | Lower, often requires significant investment to scale |
| Customer Retention (Churn Rates) | Lower churn rates indicate stable revenue (NRR ~90-125%) | Churn rates less impactful due to one-time sales |
| Market Position | Valued higher if strong market fit and competitive advantage | Valued on market penetration and competitive landscape |
| Financial Metrics | High gross margins (~80%), efficient CAC to LTV ratios | Gross margins and financial efficiency vary |
| Valuation Multiples | Higher, often 10x-15x ARR for companies with strong growth | Typically lower, based on earnings and sales |
| Investor Appeal | High due to stability and growth potential | Moderate, depends on sales and market conditions |
3 Types of Valuation Methods
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the three most commonly used valuation methods: Multiple of EBITDA, Multiple of Revenue, and Multiple of SDE (Seller’s Discretionary Earnings).
1. Multiple of EBITDA
EBITDA focuses on the core earnings of a company by removing the effects of financing, tax structures, and non-cash accounting items.
Using EBITDA multiples allows buyers to assess the company’s core profitability and compare it with peers in the industry. A higher multiple typically indicates a more valuable company.
Calculation of EBITDA for SaaS company
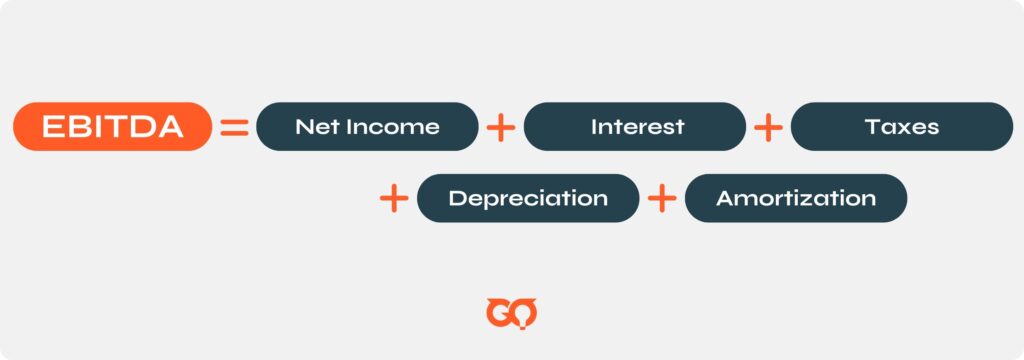
Steps to Calculate EBITDA:
- Start with Net Income: Obtain the net income from the company’s income statement.
- Add Back Interest: Include any interest expenses incurred by the company.
- Add Back Taxes: Include any taxes paid.
- Add Back Depreciation: Include depreciation expenses, which represent the reduction in value of tangible assets.
- Add Back Amortization: Include amortization expenses, which represent the reduction in value of intangible assets.
Example Calculation:
- Net Income: $500,000
- Interest: $50,000
- Taxes: $100,000
- Depreciation: $75,000
- Amortization: $25,000
EBITDA= 500,000 + 50,000 + 100,000 + 75,000 + 25,000 = $750,000
SaaS valuation using EBITDA multiple
In the SaaS industry, EBITDA multiples typically range from 6x to 12x, influenced by factors such as market position, growth trajectory, and competitive landscape. If the industry multiple is 8x:
SaaS Valuation = 750,000 × 8 = $6,000,000
2. Multiple of Revenue
Revenue multiples are especially relevant for early-stage SaaS companies that might not yet be profitable but show strong sales growth and market potential.
This method values a company based on its revenue, multiplied by a revenue multiple specific to the industry, which is straightforward and reflects the company’s sales performance.
Calculation of Revenue for SaaS company
Revenue is the total income generated by the sale of goods or services and is straightforward to obtain from the income statement.
SaaS valuation using Revenue multiple
Revenue multiples for early-stage SaaS businesses usually fall between 3x and 10x. Higher multiples are associated with companies demonstrating rapid growth, low churn rates, and high customer lifetime value.
For instance, if the annual revenue is $2,000,000 and industry multiple is 5x:
SaaS Valuation= 2,000,000 × 5 = $10,000,000
3. Multiple of SDE (Seller’s Discretionary Earnings)
Seller’s Discretionary Earnings (SDE) is a financial metric commonly used to value small to mid-sized businesses. It represents the total financial benefit that a single owner-operator would derive from the business in a year.
SDE is particularly useful for valuing businesses where the owner is heavily involved in day-to-day operations.
Calculation of SDE for SaaS company
SDE includes the business’s net income plus the owner’s compensation and benefits, and any non-essential, discretionary, or non-recurring expenses.

Steps to Calculate SDE:
- Start with Net Income: Obtain the net income from the income statement.
- Add Back Owner’s Salary: Include the owner’s salary and benefits.
- Add Back Discretionary Expenses: Include any expenses that are non-essential to the business operations (e.g., travel, meals, entertainment).
- Add Back One-Time Expenses: Include any non-recurring expenses that are not expected to continue in the future.
Example Calculation:
- Net Income: $300,000
- Owner’s Salary: $100,000
- Discretionary Expenses: $50,000
- One-Time Expenses: $20,000
So, the SDE would be:
SDE = 300,000 + 100,000 + 50,000 + 20,000 = $470,000
SaaS valuation using SDE multiple
SDE multiples usually range from 2x to 4x, depending on the business’s size, operational stability, and growth prospects. Let’s say, the industry multiple is 3x:
SaaS Valuation = 470,000 × 3 = $1,410,000
Choosing the Right Method
Selecting the appropriate valuation method depends on the stage and specific characteristics of the SaaS business:
- For mature, profitable businesses, EBITDA multiples offer a clear view of operating efficiency.
- For high-growth, early-stage companies, revenue multiples capture the potential upside in sales.
- For smaller, owner-operated businesses, SDE multiples provide a comprehensive view of the owner’s economic benefits.
How To Find Valuation Multipliers for Your SaaS?
Finding the right valuation multipliers for your SaaS business is crucial for accurate valuation. Here’s a structured approach based on key factors:
1. Revenue Size
Companies with $1-$2 million ARR often see lower multiples (3x-5x). Companies with $10 million ARR may achieve multiples of 10x-15x.
- Calculation: For a business with $5 million ARR and a 6x multiplier:
Valuation = $5,000,000 × 6 = $30,000,000
2. Net Revenue Retention (NRR)
SaaS companies with high NRR (e.g., 125%) can attract higher multiples, often between 8x and 12x. For companies with lower NRR (e.g., 90%), they may see multiples around 4x-6x.
- Calculation: If your NRR is 110% and ARR is $3 million with an 8x multiplier:
Valuation = $3,000,000 × 8 = $24,000,000
3. Churn and Renewal Rates
Companies with low churn (below 5%) and high renewal rates (above 90%) can see multiples around 7x-10x. On the contrary, higher churn rates (above 10%) and lower renewal rates (below 80%) can result in multiples around 2x-5x.
- Calculation: For a company with a 4% churn rate and $7 million ARR at a 9x multiplier:
Valuation = $7,000,000 × 9 = $63,000,000
Secondary Valuation Attributes
- Gross Margins: Higher gross margins (e.g., above 80%) can improve valuation multiples.
- Scalability: Rapid growth potential with minimal cost increase boosts multiples.
- Market Position: Strong competitive advantage can lead to higher valuation.
- Age and Stability: Older, stable companies often receive premium multiples.
- Customer Diversification: Lower customer concentration reduces risk and increases multiples.
3 Practical Tips to Increase Your SaaS Multiplier
Tip #1. Enhance Net Revenue Retention (NRR)
- Focus: Improve customer retention and upsell existing customers.
- Strategy: Implement customer success programs and regular product updates to keep users engaged and satisfied.
Start by ensuring your customers remain satisfied and engaged with your product by implementing strong customer success programs that focus on their needs and goals. Regularly update features and quickly address feedback to maintain their interest. Upsell and cross-sell relevant products and services to your existing customer base.
Tip #2. Reduce Customer Churn
- Focus: Lower the rate at which customers cancel their subscriptions.
- Strategy: Provide exceptional customer support, address feedback promptly, and offer flexible contract options.
Reducing churn is key for business stability and investor appeal. Deliver top-notch customer support and ensure a smooth user experience. Regularly gather customer feedback and use it to improve your products. This proactive approach keeps customers happy and loyal, making your business more attractive to investors.
Additionally, offering flexible contract options and personalized interactions can help retain customers longer. Consider introducing loyalty programs or tiered pricing structures that reward long-term commitments, thereby reducing churn and enhancing your multiplier.
Tip #3. Increase Gross Margins
- Focus: Improve profitability by optimizing costs.
- Strategy: Automate processes, negotiate better terms with vendors, and focus on high-margin products or services.
Improving gross margins shows better profitability, which attracts buyers. Focus on cutting costs by automating repetitive tasks and negotiating better supplier terms. Streamline operations to remove inefficiencies. Prioritize high-margin products or services to increase profitability.
For example, investing in scalable cloud infrastructure can lower operational costs, while premium service offerings can boost revenue without significantly increasing costs.
Bottom Line
How are software companies valued? It can be calculated with methods such as EBITDA, Revenue, or SDE. Understanding these concepts is crucial to improve your SaaS business’s appeal.
Boost net revenue retention, reduce churn, and increase gross margins by engaging customers, offering great support, and optimizing costs. These steps enhance business stability and investor interest.
Thank you for reading! We hope this article has been helpful for you. Stay tuned for more insights and industry knowledge on Golden Owl Digital!